Picorna viridae is divided into
five different genera: Aphtovirus, Cardiovirus,
Enterovirus, Hepatovirus, and Rhinovirus
(for more information see the Tulane
University Picorna Virus Page ). Three
of them, Enterovirus,
Rhinovirus, and Hepatovirus,
include human pathogens. See Associated
Viruses and Diseases, for a list of human viruses and diseases associated
with each genus.
Genome
ssRNA (infectious), positive sense, linear, nonsegmented, poly-A tail,
protein covalently linked at 5' end : VPg .
Morphology
icosahedral, naked, 32 capsomers made up of four polypeptides : VP1,VP2,VP3, and VP4 (12 pentons with five copies of VP1 each, 20 hexons consisting of VP2 and VP3, VP4 underneath surface of the capsid face) 7.5-8.5kb, 25-30 nm in diameter ( the smallest RNA virus), appears smooth and round under electron microscopy.
Replication
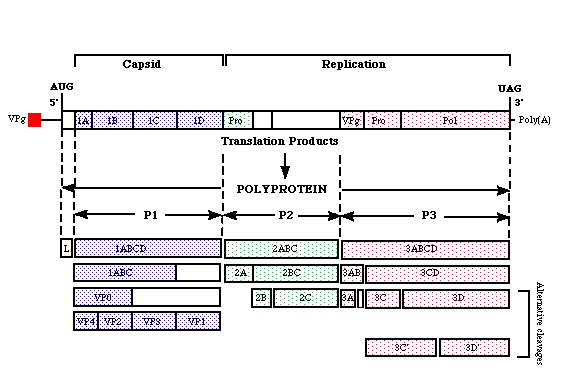
Replication takes place in the cytoplasm. The positive sense single
stranded RNA functions as mRNA and therefore does not require transcriptase
in the virion. Following adsorption, penetration, and uncoating VPg
is removed by enzymes and the mRNA is translated into a polyprotein; it
is then cleaved into P1,P2, and P3 which act as intermediates. They
are further cleaved to eventually form structural and nonstructural proteins
as well as an RNA dependent RNA polymerase (VP4,VP2,VP3,VP1,2A,2B,2C,3A,VPg,3C,
and 3D). Synthesis of the complementary strand uses the VPg protein
as a primer and is initiated at the 3' end. This strand acts as a
template for the virion RNA. (see diagram below)
